Introduction
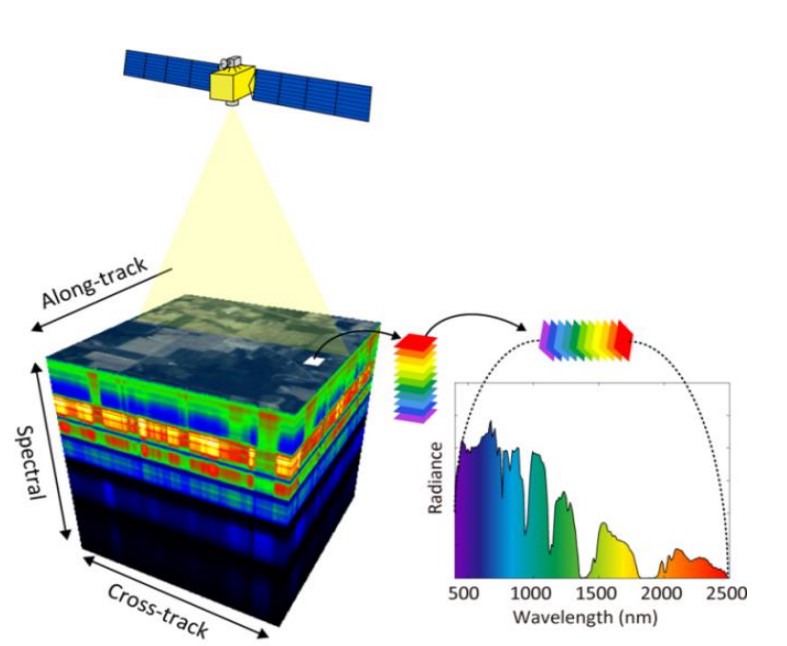
Hyperspectral imaging (HSI) has emerged as a transformative technology in the field of earth observation. By capturing information across hundreds of spectral bands, HSI allows us to analyze and interpret data with unparalleled precision. As we enter this new era, hyperspectral imaging is set to revolutionize how we monitor, manage, and protect our planet.
What is Hyperspectral Imaging?
Unlike traditional imaging systems that capture data in three to ten spectral bands (e.g., RGB), hyperspectral sensors divide the spectrum into hundreds of contiguous bands. This capability provides detailed spectral signatures for every pixel in an image, enabling the identification and differentiation of materials and substances.
The Technology Behind Hyperspectral Imaging
- Hyperspectral Sensors: Operate across visible, near-infrared, and shortwave infrared wavelengths.
- Key Features: High spectral resolution, spatial accuracy, and the ability to detect subtle variations in material composition.
- Platform Integration: HSI is deployed on satellites, drones, and aircraft, enhancing its flexibility and application potential.
Applications of Hyperspectral Imaging
- Agriculture and Food Security:
- Monitoring crop health and nutrient levels.
- Detecting diseases, pests, and water stress.
- Precision farming to optimize resource use.
- Environmental Monitoring:
- Identifying pollutants and contaminants in water and soil.
- Tracking deforestation and land degradation.
- Monitoring coastal ecosystems and coral reefs.
- Mineral Exploration:
- Mapping mineral deposits and distinguishing between rock types.
- Reducing exploration costs by improving target identification.
- Disaster Management:
- Assessing areas affected by wildfires, floods, and landslides.
- Supporting rapid response efforts during natural disasters.
- Defense and Surveillance:
- Enhancing situational awareness by identifying camouflaged targets.
- Supporting border security with advanced detection capabilities.
Recent Developments in Hyperspectral Imaging
- Satellite Missions:
- The European Space Agency’s EnMAP and the Italian Space Agency’s PRISMA are setting new benchmarks in hyperspectral remote sensing.
- Upcoming missions like NASA’s SBG (Surface Biology and Geology) are poised to expand the applications of HSI.
- AI and Machine Learning:
- Automated feature extraction using AI is making hyperspectral data analysis faster and more accurate.
- Machine learning algorithms are enabling real-time processing and decision-making.
- Miniaturization of Sensors:
- Compact hyperspectral sensors are being integrated into UAVs, democratizing access to this advanced technology.
Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges:
- Data Volume: Hyperspectral data requires significant storage and computational power.
- Cost: High costs associated with sensor development and deployment.
- Standardization: Lack of global standards for hyperspectral data processing.
Opportunities:
- Commercial Applications: Expanding use in precision agriculture, environmental management, and resource exploration.
- Collaboration: Partnerships between governments, academia, and private companies to advance technology and applications.
- AI Integration: Leveraging AI to simplify data analysis and expand usability.
Conclusion
The era of hyperspectral imaging is truly upon us, with transformative applications spanning agriculture, environmental management, defense, and beyond. As technology continues to advance, hyperspectral imaging will play an increasingly critical role in addressing global challenges, from food security to climate change. This is not just a step forward in earth observation; it is a leap toward a deeper understanding of our planet.