Introduction
Geospatial data has been at the heart of technological advances across industries, enabling applications ranging from smart cities to disaster management. As we move into 2025, the landscape of geospatial technology is evolving at an unprecedented pace. Emerging trends, new technologies, and innovative applications are poised to redefine how geospatial data is captured, processed, and utilized.
This article explores the next frontier in geospatial data, offering a glimpse into the breakthroughs shaping 2025 and beyond.
Key Trends Shaping Geospatial Data in 2025
1. Integration of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming geospatial analytics by automating processes and uncovering patterns in massive datasets.
- Applications: Predictive analytics for urban planning, climate modeling, and disaster risk management.
- Advancements: AI-driven real-time analysis, enabling quicker decision-making during emergencies.
2. Real-Time Geospatial Data Streams
The proliferation of IoT devices and advancements in sensor technologies have enabled the generation of real-time geospatial data streams.
- Examples: Traffic monitoring systems, weather forecasting models, and precision agriculture sensors.
- Impact: Enhanced situational awareness and proactive decision-making.
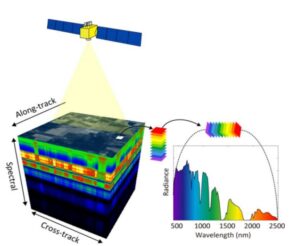
3. High-Resolution Imaging and Mapping
2025 is set to witness significant improvements in the resolution and accuracy of geospatial data.
- Hyperspectral Imaging: Capturing hundreds of spectral bands for detailed material analysis.
- LiDAR Technology: Generating high-resolution 3D models for urban planning and forestry management.
4. Democratization of Geospatial Data
The rise of open-source platforms and collaborative initiatives is making geospatial data more accessible.
- Open Data Initiatives: Platforms like OpenStreetMap and Digital Earth Africa.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: Platforms like Google Earth Engine democratize high-performance geospatial analysis.
Emerging Technologies Driving the Next Frontier
Satellite Mega-Constellations
Companies like SpaceX, Amazon, and Planet are launching constellations of small satellites.
- Capabilities: High revisit rates and global coverage.
- Applications: Continuous monitoring of environmental changes, urban expansion, and agricultural productivity.
Quantum Computing in Geospatial Analytics
Quantum computing holds the potential to revolutionize geospatial data processing.
- Advantage: Handling complex geospatial simulations and optimization problems at unprecedented speeds.
- Future Applications: Advanced weather prediction models and large-scale urban simulations.
Blockchain for Geospatial Data Security
Blockchain technology is emerging as a solution for securing geospatial data transactions.Use Cases: Verifying the authenticity of geospatial datasets, preventing tampering, and enhancing transparency in data sharing
Challenges to Overcome
Despite these advancements, several challenges remain:
- Data Overload: Managing and processing the ever-growing volume of geospatial data.
- Interoperability: Ensuring seamless integration between diverse data sources and formats.
- Ethical Concerns: Balancing innovation with privacy and ethical considerations in data usage.
The Future of Geospatial Data
As we look ahead to 2025, the convergence of cutting-edge technologies promises to unlock new possibilities in geospatial data. From real-time analytics to global monitoring systems, the next frontier is about leveraging geospatial intelligence to address the world’s most pressing challenges, including climate change, urbanization, and resource management.
By staying at the forefront of these trends, professionals and organizations can harness the power of geospatial data to shape a smarter, more sustainable future.